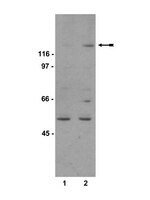
Calcimimetic R-568 and its enantiomer S-568 increase nitric oxide release in human endothelial cells.
Bonomini, M; Giardinelli, A; Morabito, C; Di Silvestre, S; Di Cesare, M; Di Pietro, N; Sirolli, V; Formoso, G; Amoroso, L; Mariggiò, MA; Pandolfi, A
PloS one
7
e30682
2012
Show Abstract
Calcimimetics, such as R-568, are thought to activate G protein-linked Ca(2+)-sensing receptor (CaSR) by allosterically increasing the affinity of the receptor for Ca(2+) allowing for efficient control of uremic hyperparathyroidism. Several recent studies suggest they possess additional vascular actions. Although it has been postulated that calcimimetics may have a direct effect on CaSR in the blood vessels, further studies are needed to elucidate their vascular CaSR-dependent versus CaSR-independent effects.Focusing on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), we studied the CaSR expression and distribution by Immunofluorescence and Western Blot analysis. CaSR function was evaluated by measuring the potential effect of calcimimetic R-568 and its enantiomer S-568 upon the modulation of intracellular Ca(2+) levels (using a single cell approach and FURA-2AM), in the presence or absence of Calhex-231, a negative modulator of CaSR. To address their potential vascular functions, we also evaluated R- and S-568-stimulated enzymatic release of Nitric Oxide (NO) by DAF-2DA, by Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) radiometric assay (both in HUVECs and in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells) and by measuring eNOS-ser1177 phosphorylation levels (Immunoblotting). We show that, although the CaSR protein was expressed in HUVECs, it was mainly distributed in cytoplasm while the functional CaSR dimers, usually localized on the plasma membrane, were absent. In addition, regardless of the presence or absence of Calhex-231, both R- and S-568 significantly increased intracellular Ca(2+) levels by mobilization of Ca(2+) from intracellular stores, which in turn augmented NO release by a time- and Ca(2+)-dependent increase in eNOS-ser1177 phosphorylation levels.Taken together, these data indicate that in human endothelium there is no stereoselectivity in the responses to calcimimetics and that CaSR is probably not involved in the action of R- and S-568. This suggests an additional mechanism in support of the CaSR-independent role of calcimimetics as vasculotrope agents. | Western Blotting | Human | 22295103
 |
Src kinase activates endothelial nitric-oxide synthase by phosphorylating Tyr-83.
Fulton, D; Church, JE; Ruan, L; Li, C; Sood, SG; Kemp, BE; Jennings, IG; Venema, RC
The Journal of biological chemistry
280
35943-52
2005
Show Abstract
The endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) is regulated in part by serine/threonine phosphorylation, but eNOS tyrosine phosphorylation is less well understood. In the present study we have examined the tyrosine phosphorylation of eNOS in bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) exposed to oxidant stress. Hydrogen peroxide and pervanadate (PV) treatment stimulates eNOS tyrosine phosphorylation in BAECs. Phosphorylation is blocked by the Src kinase family inhibitor, 4-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine (PP2). Moreover, eNOS and c-Src can be coimmunoprecipitated from BAEC lysates by antibodies directed against either protein. Domain mapping and site-directed mutagenesis studies in COS-7 cells transfected with either eNOS alone and then treated with PV or cotransfected with eNOS and constitutively active v-Src identified Tyr-83 (bovine sequence) as the major eNOS tyrosine phosphorylation site. Tyr-83 phosphorylation is associated with a 3-fold increase in basal NO release from cotransfected cells. Furthermore, the Y83F eNOS mutation attenuated thapsigargin-stimulated NO production. Taken together, these data indicate that Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of eNOS at Tyr-83 modulates eNOS activity in endothelial cells. | | | 16123043
 |
Acute activation and phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.
Harris, MB; Blackstone, MA; Sood, SG; Li, C; Goolsby, JM; Venema, VJ; Kemp, BE; Venema, RC
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology
287
H560-6
2004
Show Abstract
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase inhibitors, statins, provide beneficial effects independent of their lipid-lowering effects. One beneficial effect appears to involve acute activation of endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase (eNOS) and increased NO release. However, the mechanism of acute statin-stimulated eNOS activation is unknown. Therefore, we hypothesized that eNOS activation may be coupled to altered eNOS phosphorylation. Bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs), passages 2-6, were treated with either lovastatin or pravastatin from 0 to 30 min. eNOS phosphorylation was examined by Western blot by use of phosphospecific antibodies for Ser-1179, Ser-635, Ser-617, Thr-497, and Ser-116. Statin stimulation of BAECs increased eNOS phosphorylation at Ser-1179 and Ser-617, which was blocked by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase)/Akt inhibitor wortmannin, and at Ser-635, which was blocked by the protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor KT-5720. Statin treatment of BAECs transiently increased NO release by fourfold, measured by cGMP accumulation, and was attenuated by N-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester, wortmannin, and KT-5720 but not by mevalonate. In conclusion, these data demonstrate that eNOS is acutely activated by statins independent of HMG-CoA reductase inhibition and that in addition to Ser-1179, eNOS phosphorylation at Ser-635 and Ser-617 through PKA and Akt, respectively, may explain, in part, a mechanism by which eNOS is activated in response to acute statin treatment. | | | 15087285
 |
AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation of endothelial NO synthase.
Chen, Z P, et al.
FEBS Lett., 443: 285-9 (1999)
1999
Show Abstract
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in rat skeletal and cardiac muscle is activated by vigorous exercise and ischaemic stress. Under these conditions AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase causing increased oxidation of fatty acids. Here we show that AMPK co-immunoprecipitates with cardiac endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) and phosphorylates Ser-1177 in the presence of Ca2+-calmodulin (CaM) to activate eNOS both in vitro and during ischaemia in rat hearts. In the absence of Ca2+-calmodulin, AMPK also phosphorylates eNOS at Thr-495 in the CaM-binding sequence, resulting in inhibition of eNOS activity but Thr-495 phosphorylation is unchanged during ischaemia. Phosphorylation of eNOS by the AMPK in endothelial cells and myocytes provides a further regulatory link between metabolic stress and cardiovascular function. | | | 10025949
 |
The Akt kinase signals directly to endothelial nitric oxide synthase.
Michell, B J, et al.
Curr. Biol., 9: 845-8 (1999)
1999
Show Abstract
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) is an important modulator of angiogenesis and vascular tone [1]. It is stimulated by treatment of endothelial cells in a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase)-dependent fashion by insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [2] [3] and is activated by phosphorylation at Ser1177 in the sequence RIRTQS(1177)F (in the single-letter amino acid code) [4]. The protein kinase Akt is an important downstream target of PI 3-kinase [5] [6], regulating VEGF-stimulated endothelial cell survival [7]. Akt phosphorylates substrates within a defined motif [8], which is present in the sequence surrounding Ser1177 in eNOS. Both Akt [5] [6] and eNOS [9] are localized to, and activated at, the plasma membrane. We found that purified Akt phosphorylated cardiac eNOS at Ser1177, resulting in activation of eNOS. Phosphorylation at this site was stimulated by treatment of bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) with VEGF or IGF-1, and Akt was activated in parallel. Preincubation with wortmannin, an inhibitor of Akt signalling, reduced VEGF- or IGF-1-induced Akt activity and eNOS phosphorylation. Akt was detected in immunoprecipitates of eNOS from BAECs, and eNOS in immunoprecipitates of Akt, indicating that the two enzymes associate in vivo. It is thus apparent that Akt directly activates eNOS in endothelial cells. These results strongly suggest that Akt has an important role in the regulation of normal angiogenesis and raise the possibility that the enhanced activity of this kinase that occurs in carcinomas may contribute to tumor vascularization and survival. | | | 10469573
 |