The Nucleosome Acidic Patch Regulates the H2B K123 Monoubiquitylation Cascade and Transcription Elongation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Cucinotta, CE; Young, AN; Klucevsek, KM; Arndt, KM
PLoS genetics
11
e1005420
2015
Show Abstract
Eukaryotes regulate gene expression and other nuclear processes through the posttranslational modification of histones. In S. cerevisiae, the mono-ubiquitylation of histone H2B on lysine 123 (H2B K123ub) affects nucleosome stability, broadly influences gene expression and other DNA-templated processes, and is a prerequisite for additional conserved histone modifications that are associated with active transcription, namely the methylation of lysine residues in H3. While the enzymes that promote these chromatin marks are known, regions of the nucleosome required for the recruitment of these enzymes are undefined. To identify histone residues required for H2B K123ub, we exploited a functional interaction between the ubiquitin-protein ligase, Rkr1/Ltn1, and H2B K123ub in S. cerevisiae. Specifically, we performed a synthetic lethal screen with cells lacking RKR1 and a comprehensive library of H2A and H2B residue substitutions, and identified H2A residues that are required for H2B K123ub. Many of these residues map to the nucleosome acidic patch. The substitutions in the acidic patch confer varying histone modification defects downstream of H2B K123ub, indicating that this region contributes differentially to multiple histone modifications. Interestingly, substitutions in the acidic patch result in decreased recruitment of H2B K123ub machinery to active genes and defects in transcription elongation and termination. Together, our findings reveal a role for the nucleosome acidic patch in recruitment of histone modification machinery and maintenance of transcriptional integrity. | | | 26241481
 |
The ASH1-RELATED3 SET-domain protein controls cell division competence of the meristem and the quiescent center of the Arabidopsis primary root.
Kumpf, R; Thorstensen, T; Rahman, MA; Heyman, J; Nenseth, HZ; Lammens, T; Herrmann, U; Swarup, R; Veiseth, SV; Emberland, G; Bennett, MJ; De Veylder, L; Aalen, RB
Plant physiology
166
632-43
2014
Show Abstract
The stem cell niche of the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) primary root apical meristem is composed of the quiescent (or organizing) center surrounded by stem (initial) cells for the different tissues. Initial cells generate a population of transit-amplifying cells that undergo a limited number of cell divisions before elongating and differentiating. It is unclear whether these divisions occur stochastically or in an orderly manner. Using the thymidine analog 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine to monitor DNA replication of cells of Arabidopsis root meristems, we identified a pattern of two, four, and eight neighboring cells with synchronized replication along the cortical, epidermal, and endodermal cell files, suggested to be daughters, granddaughters, and great-granddaughters of the direct progeny of each stem cell. Markers of mitosis and cytokinesis were not present in the region closest to the transition zone where the cells start to elongate, suggesting that great-granddaughter cells switch synchronously from the mitotic cell cycle to endoreduplication. Mutations in the stem cell niche-expressed ASH1-RELATED3 (ASHR3) gene, encoding a SET-domain protein conferring histone H3 lysine-36 methylation, disrupted this pattern of coordinated DNA replication and cell division and increased the cell division rate in the quiescent center. E2Fa/E2Fb transcription factors controlling the G1-to-S-phase transition regulate ASHR3 expression and bind to the ASHR3 promoter, substantiating a role for ASHR3 in cell division control. The reduced length of the root apical meristem and primary root of the mutant ashr3-1 indicate that synchronization of replication and cell divisions is required for normal root growth and development. | | | 25034019
 |
The demethylase JMJD2C localizes to H3K4me3-positive transcription start sites and is dispensable for embryonic development.
Pedersen, MT; Agger, K; Laugesen, A; Johansen, JV; Cloos, PA; Christensen, J; Helin, K
Molecular and cellular biology
34
1031-45
2014
Show Abstract
The histone demethylase JMJD2C, also known as KDM4C/GASC1, has activity against methylated H3K9 and H3K36 and is amplified and/or overexpressed in human cancers. By the generation of Jmjd2c knockout mice, we demonstrate that loss of Jmjd2c is compatible with cellular proliferation, embryonic stem cell (ESC) self-renewal, and embryonic development. Moreover, we report that JMJD2C localizes to H3K4me3-positive transcription start sites in both primary cells and in the human carcinoma KYSE150 cell line containing an amplification of the JMJD2C locus. Binding is dependent on the double Tudor domain of JMJD2C, which recognizes H3K4me3 but not H4K20me2/me3 in vitro, showing a binding specificity different from that of the double Tudor domains of JMJD2A and JMJD2B. Depletion of JMJD2C in KYSE150 cells has a modest effect on H3K9me3 and H3K36me3 levels but impairs proliferation and leads to deregulated expression of a subset of target genes involved in cell cycle progression. Taking these findings together, we show that JMJD2C is targeted to H3K4me3-positive transcription start sites, where it can contribute to transcriptional regulation, and report that the putative oncogene JMJD2C generally is not required for cellular proliferation or embryonic development. | | | 24396064
 |
dRYBP counteracts chromatin-dependent activation and repression of transcription.
Fereres, S; Simón, R; Mohd-Sarip, A; Verrijzer, CP; Busturia, A
PloS one
9
e113255
2014
Show Abstract
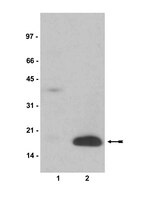
Chromatin dependent activation and repression of transcription is regulated by the histone modifying enzymatic activities of the trithorax (trxG) and Polycomb (PcG) proteins. To investigate the mechanisms underlying their mutual antagonistic activities we analyzed the function of Drosophila dRYBP, a conserved PcG- and trxG-associated protein. We show that dRYBP is itself ubiquitylated and binds ubiquitylated proteins. Additionally we show that dRYBP maintains H2A monoubiquitylation, H3K4 monomethylation and H3K36 dimethylation levels and does not affect H3K27 trimethylation levels. Further we show that dRYBP interacts with the repressive SCE and dKDM2 proteins as well as the activating dBRE1 protein. Analysis of homeotic phenotypes and post-translationally modified histones levels show that dRYBP antagonizes dKDM2 and dBRE1 functions by respectively preventing H3K36me2 demethylation and H2B monoubiquitylation. Interestingly, our results show that inactivation of dBRE1 produces trithorax-like related homeotic transformations, suggesting that dBRE1 functions in the regulation of homeotic genes expression. Our findings indicate that dRYBP regulates morphogenesis by counteracting transcriptional repression and activation. Thus, they suggest that dRYBP may participate in the epigenetic plasticity important during normal and pathological development. | Western Blotting | | 25415640
 |
Distinct structural transitions of chromatin topological domains correlate with coordinated hormone-induced gene regulation.
Le Dily, F; Baù, D; Pohl, A; Vicent, GP; Serra, F; Soronellas, D; Castellano, G; Wright, RH; Ballare, C; Filion, G; Marti-Renom, MA; Beato, M
Genes & development
28
2151-62
2014
Show Abstract
The human genome is segmented into topologically associating domains (TADs), but the role of this conserved organization during transient changes in gene expression is not known. Here we describe the distribution of progestin-induced chromatin modifications and changes in transcriptional activity over TADs in T47D breast cancer cells. Using ChIP-seq (chromatin immunoprecipitation combined with high-throughput sequencing), Hi-C (chromosome capture followed by high-throughput sequencing), and three-dimensional (3D) modeling techniques, we found that the borders of the ∼ 2000 TADs in these cells are largely maintained after hormone treatment and that up to 20% of the TADs could be considered as discrete regulatory units where the majority of the genes are either transcriptionally activated or repressed in a coordinated fashion. The epigenetic signatures of the TADs are homogeneously modified by hormones in correlation with the transcriptional changes. Hormone-induced changes in gene activity and chromatin remodeling are accompanied by differential structural changes for activated and repressed TADs, as reflected by specific and opposite changes in the strength of intra-TAD interactions within responsive TADs. Indeed, 3D modeling of the Hi-C data suggested that the structure of TADs was modified upon treatment. The differential responses of TADs to progestins and estrogens suggest that TADs could function as "regulons" to enable spatially proximal genes to be coordinately transcribed in response to hormones. | | | 25274727
 |
NuA4 links methylation of histone H3 lysines 4 and 36 to acetylation of histones H4 and H3.
Ginsburg, DS; Anlembom, TE; Wang, J; Patel, SR; Li, B; Hinnebusch, AG
The Journal of biological chemistry
289
32656-70
2014
Show Abstract
Cotranscriptional methylation of histone H3 lysines 4 and 36 by Set1 and Set2, respectively, stimulates interaction between nucleosomes and histone deacetylase complexes to block cryptic transcription in budding yeast. We previously showed that loss of all H3K4 and H3K36 methylation in a set1Δset2Δ mutant reduces interaction between native nucleosomes and the NuA4 lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) complex. We now provide evidence that NuA4 preferentially binds H3 tails mono- and dimethylated on H3K4 and di- and trimethylated on H3K36, an H3 methylation pattern distinct from that recognized by the RPD3C(S) and Hos2/Set3 histone deacetylase complexes (HDACs). Loss of H3K4 or H3K36 methylation in set1Δ or set2Δ mutants reduces NuA4 interaction with bulk nucleosomes in vitro and in vivo, and reduces NuA4 occupancy of transcribed coding sequences at particular genes. We also provide evidence that NuA4 acetylation of lysine residues in the histone H4 tail stimulates SAGA interaction with nucleosomes and its recruitment to coding sequences and attendant acetylation of histone H3 in vivo. Thus, H3 methylation exerts opposing effects of enhancing nucleosome acetylation by both NuA4 and SAGA as well as stimulating nucleosome deacetylation by multiple HDACs to maintain the proper level of histone acetylation in transcribed coding sequences. | | | 25301943
 |
Histone methyltransferase MMSET/NSD2 alters EZH2 binding and reprograms the myeloma epigenome through global and focal changes in H3K36 and H3K27 methylation.
Popovic, R; Martinez-Garcia, E; Giannopoulou, EG; Zhang, Q; Zhang, Q; Ezponda, T; Shah, MY; Zheng, Y; Will, CM; Small, EC; Hua, Y; Bulic, M; Jiang, Y; Carrara, M; Calogero, RA; Kath, WL; Kelleher, NL; Wang, JP; Elemento, O; Licht, JD
PLoS genetics
10
e1004566
2014
Show Abstract
Overexpression of the histone methyltransferase MMSET in t(4;14)+ multiple myeloma patients is believed to be the driving factor in the pathogenesis of this subtype of myeloma. MMSET catalyzes dimethylation of lysine 36 on histone H3 (H3K36me2), and its overexpression causes a global increase in H3K36me2, redistributing this mark in a broad, elevated level across the genome. Here, we demonstrate that an increased level of MMSET also induces a global reduction of lysine 27 trimethylation on histone H3 (H3K27me3). Despite the net decrease in H3K27 methylation, specific genomic loci exhibit enhanced recruitment of the EZH2 histone methyltransferase and become hypermethylated on this residue. These effects likely contribute to the myeloma phenotype since MMSET-overexpressing cells displayed increased sensitivity to EZH2 inhibition. Furthermore, we demonstrate that such MMSET-mediated epigenetic changes require a number of functional domains within the protein, including PHD domains that mediate MMSET recruitment to chromatin. In vivo, targeting of MMSET by an inducible shRNA reversed histone methylation changes and led to regression of established tumors in athymic mice. Together, our work elucidates previously unrecognized interplay between MMSET and EZH2 in myeloma oncogenesis and identifies domains to be considered when designing inhibitors of MMSET function. | Western Blotting | | 25188243
 |
Histone H3.3 and its proteolytically processed form drive a cellular senescence programme.
Duarte, LF; Young, AR; Wang, Z; Wu, HA; Panda, T; Kou, Y; Kapoor, A; Hasson, D; Mills, NR; Ma'ayan, A; Narita, M; Bernstein, E
Nature communications
5
5210
2014
Show Abstract
The process of cellular senescence generates a repressive chromatin environment, however, the role of histone variants and histone proteolytic cleavage in senescence remains unclear. Here, using models of oncogene-induced and replicative senescence, we report novel histone H3 tail cleavage events mediated by the protease Cathepsin L. We find that cleaved forms of H3 are nucleosomal and the histone variant H3.3 is the preferred cleaved form of H3. Ectopic expression of H3.3 and its cleavage product (H3.3cs1), which lacks the first 21 amino acids of the H3 tail, is sufficient to induce senescence. Further, H3.3cs1 chromatin incorporation is mediated by the HUCA histone chaperone complex. Genome-wide transcriptional profiling revealed that H3.3cs1 facilitates transcriptional silencing of cell cycle regulators including RB/E2F target genes, likely via the permanent removal of H3K4me3. Collectively, our study identifies histone H3.3 and its proteolytically processed forms as key regulators of cellular senescence. | | | 25394905
 |
The histone methyltransferase MMSET regulates class switch recombination.
Pei, H; Wu, X; Liu, T; Yu, K; Jelinek, DF; Lou, Z
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950)
190
756-63
2013
Show Abstract
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) is a genetic disease with characteristic facial features and developmental disorders. Of interest, loss of the MMSET gene (also known as WHSC1) is considered to be responsible for the core phenotypes of this disease. Patients with WHS also display Ab deficiency, although the underlying cause of this deficiency is unclear. Recent studies suggest that the histone methyltransferase activity of MMSET plays an important role in the DNA damage response by facilitating the recruitment of 53BP1 to sites of DNA damage. We hypothesize that MMSET also regulates class switch recombination (CSR) through its effect on 53BP1. In this study, we show that MMSET indeed plays an important role in CSR through its histone methyltransferase activity. Knocking down MMSET expression impaired 53BP1 recruitment as well as the germline transcription of the Igh switch regions, resulting in defective CSR but no effect on cell growth and viability. These results suggest that defective CSR caused by MMSET deficiency could be a cause of Ab deficiency in WHS patients. | | | 23241889
 |
Inhibition of PRC2 histone methyltransferase activity increases TRAIL-mediated apoptosis sensitivity in human colon cancer cells.
Benoit, YD; Laursen, KB; Witherspoon, MS; Lipkin, SM; Gudas, LJ
Journal of cellular physiology
228
764-72
2013
Show Abstract
Colorectal cancer is ranked among the top leading causes of cancer death in industrialized populations. Polycomb group proteins, including Suz12 and Ezh2, are epigenetic regulatory proteins that act as transcriptional repressors of many differentiation-associated genes and are overexpressed in a large subset of colorectal cancers. Retinoic acid (RA) acts as a negative regulator of PcG actions in stem cells, but has shown limited therapeutic potential in some solid tumors, including colorectal cancer, in part because of retinoic acid receptor β silencing. Through treatment with RA, Suz12 shRNA knockdown, or Ezh2 pharmacological inhibition with 3-deazaneplanocin A (DZNep), we increased TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cell lines. This increased apoptosis in human colon cancer cells after RA or DZNep treatment was associated with a ~2.5-fold increase in TNFRSF10B (DR5) transcript levels and a 42% reduction in the H3K27me3 epigenetic mark at the TNFRSF10B promoter after DZNep addition. Taken together, our findings indicate that pharmacological inhibition of Polycomb repressive complex 2 histone methyltransferase activity may constitute a new epigenetic therapeutic strategy to overcome RA non-responsiveness in a subset of colorectal tumors by increasing TRAIL-mediated apoptosis sensitivity. | Western Blotting | | 23001792
 |