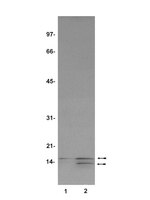
Phosphorylation and arginine methylation mark histone H2A prior to deposition during Xenopus laevis development.
Wang, WL; Anderson, LC; Nicklay, JJ; Chen, H; Gamble, MJ; Shabanowitz, J; Hunt, DF; Shechter, D
2014
|
 |
Analysis of histones in Xenopus laevis. I. A distinct index of enriched variants and modifications exists in each cell type and is remodeled during developmental transitions.
Shechter, D; Nicklay, JJ; Chitta, RK; Shabanowitz, J; Hunt, DF; Allis, CD
2009
| 18957438 |
Phosphorylation of histone H2A by protein kinase C and identification of the phosphorylation site.
Takeuchi, F, et al.
J. Biochem., 111: 788-92 (1992)
1992
Show Abstract
In regenerating rat liver, nuclear protein histone H2A was shown to be phosphorylated on its amino-terminal serine residue [Sung et al. (1971) J. Biol. Chem. 246, 1358-1364], but the protein kinase which phosphorylates this residue has not been identified. To evaluate the possibility that protein kinase C can phosphorylate this residue, calf thymus histone H2A was 32P-labeled by incubation with [gamma-32P]ATP and highly purified protein kinase C from rat brain in the presence of calcium and phospholipid. About 1 mol of 32P was incorporated per mol of histone H2A and the Km and apparent Vmax of the reaction were calculated to be 2.1 microM and 0.35 mumol/min/mg, respectively. So histone H2A seemed to be a good substrate for protein kinase C. Further, the proteolytic phosphopeptides of 32P-labeled histone H2A were isolated by means of a series of column chromatographies and analyzed for their amino acid compositions. Comparison of the data with the known primary structure of histone H2A revealed their amino acid sequence as 1Ser-Gly-Arg. These data suggest that protein kinase C may be a candidate for the protein kinase which phosphorylates the amino-terminal serine residue of histone H2A during the regeneration of rat liver. | 1500420
 |