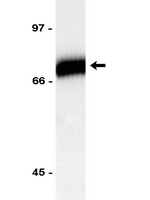
TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) controls cell survival through PAI-2/serpinB2 and transglutaminase 2.
Delhase, M; Kim, SY; Lee, H; Naiki-Ito, A; Chen, Y; Ahn, ER; Murata, K; Kim, SJ; Lautsch, N; Kobayashi, KS; Shirai, T; Karin, M; Nakanishi, M
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
109
E177-86
2012
Show Abstract
The decision between survival and death in cells exposed to TNF relies on a highly regulated equilibrium between proapoptotic and antiapoptotic factors. The TNF-activated antiapoptotic response depends on several transcription factors, including NF-κB and its RelA/p65 subunit, that are activated through phosphorylation-mediated degradation of IκB inhibitors, a process controlled by the IκB kinase complex. Genetic studies in mice have identified the IκB kinase-related kinase TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1; also called NAK or T2K) as an additional regulatory molecule that promotes survival downstream of TNF, but the mechanism through which TBK1 exerts its survival function has remained elusive. Here we show that TBK1 triggers an antiapoptotic response by controlling a specific RelA/p65 phosphorylation event. TBK1-induced RelA phosphorylation results in inducible expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 (PAI-2), a member of the serpin family with known antiapoptotic activity. PAI-2 limits caspase-3 activation through stabilization of transglutaminase 2 (TG2), which cross-links and inactivates procaspase-3. Importantly, Tg2(-/-) mice were found to be more susceptible to apoptotic cell death in two models of TNF-dependent acute liver injury. Our results establish PAI-2 and TG2 as downstream mediators in the antiapoptotic response triggered upon TBK1 activation. | | 22203995
 |
Increase in endoplasmic reticulum-associated tissue transglutaminase and enzymatic activation in a cellular model of Parkinson's disease.
Robin Verhaar,Benjamin Drukarch,John G J M Bol,Cornelis A M Jongenelen,René J P Musters,Micha M M Wilhelmus
Neurobiology of disease
45
2012
Show Abstract
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by accumulation of α-synuclein aggregates and degeneration of melanized, catecholaminergic neurons. The tissue transglutaminase (tTG) enzyme catalyzes molecular protein cross-linking. In PD, tTG levels are increased and cross-linking has been identified as an important factor in α-synuclein aggregation. In our quest to link tTGs distribution in the human brain to the hallmarks of PD pathology, we recently reported that catecholaminergic neurons in PD disease-affected brain areas display typical endoplasmic reticulum (ER) granules showing tTG immunoreactivity. In the present study, we set out to elucidate the nature of the interaction between tTG and the ER in PD pathogenesis, using retinoic-acid differentiated SH-SY5Y cells exposed to the PD-mimetic 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP(+)). Alike our observations in PD brain, MPP(+)-treated cells displayed typical TG-positive granules, that were also induced by other PD mimetics and by ER-stress inducing toxins. Additional immunocytochemical and biochemical investigation revealed that tTG is indeed associated to the ER, in particular at the cytoplasmic face of the ER. Upon MPP(+) exposure, additional recruitment of tTG toward the ER was found. In addition, we observed that MPP(+)-induced tTG activity results in transamidation of ER membrane proteins, like calnexin. Our data provide strong evidence for a, so far unrecognized, localization of tTG at the ER, at least in catecholaminergic neurons, and suggests that in PD activation of tTG may have a direct impact on ER function, in particular via post-translational modification of ER membrane proteins. | | 22051113
 |
Quantitative protein and mRNA profiling shows selective post-transcriptional control of protein expression by vasopressin in kidney cells.
Khositseth, S; Pisitkun, T; Slentz, DH; Wang, G; Hoffert, JD; Knepper, MA; Yu, MJ
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP
10
M110.004036
2011
Show Abstract
Previous studies in yeast have supported the view that post-transcriptional regulation of protein abundances may be more important than previously believed. Here we ask the question: "In a physiological regulatory process (the response of mammalian kidney cells to the hormone vasopressin), what fraction of the expressed proteome undergoes a change in abundance and what fraction of the regulated proteins have corresponding changes in mRNA levels?" In humans and other mammals, vasopressin fulfills a vital homeostatic role (viz. regulation of renal water excretion) by regulating the water channel aquaporin-2 in collecting duct cells. To address the question posed, we utilized large-scale quantitative protein mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) employing stable isotopic labeling in cultured mpkCCD cells ('SILAC') coupled with transcriptomic profiling using oligonucleotide expression arrays (Affymetrix). Preliminary studies analyzing two nominally identical control samples by SILAC LC-MS/MS yielded a relative S.D. of 13% (for ratios), establishing the precision of the SILAC approach in our hands. We quantified nearly 3000 proteins with nontargeted SILAC LC-MS/MS, comparing vasopressin- versus vehicle-treated samples. Of these proteins 786 of them were quantified in each of 3 experiments, allowing statistical analysis and 188 of these showed significant vasopressin-induced changes in abundance, including aquaporin-2 (20-fold increase). Among the proteins with statistically significant abundance changes, a large fraction (at least one-third) was found to lack changes in the corresponding mRNA species (despite sufficient statistical power), indicating that post-transcriptional regulation of protein abundance plays an important role in the vasopressin response. Bioinformatic analysis of the regulated proteins (versus all transcripts) shows enrichment of glutathione S-transferase isoforms as well as proteins involved in organization of the actin cytoskeleton. The latter suggests that long-term regulatory processes may contribute to actomyosin-dependent trafficking of the water channel aquaporin-2. The results provide impetus for increased focus on translational regulation and regulation of protein degradation in physiological control in mammalian epithelial cells. | | 20940332
 |
Regulation of ATPase activity of transglutaminase 2 by MT1-MMP: implications for mineralization of MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cultures.
Yukiko Nakano,Jennifer Forsprecher,Mari T Kaartinen
Journal of cellular physiology
223
2010
Show Abstract
A pro-mineralization function for transglutaminase 2 (TG2) has been suggested in numerous studies related to bone, cartilage, and vascular calcification. TG2 is an enzyme which can perform protein crosslinking functions, or act as a GTPase/ATPase depending upon different stimuli. We have previously demonstrated that TG2 can act as an ATPase in a Ca(2+)-rich environment and that it can regulate phosphate levels in osteoblast cultures. In this study, we investigate the role MT1-MMP in regulating the ATPase activity of TG2. We report that proteolytic cleavage of TG2 by MT1-MMP in vitro results in nearly a 3-fold increase in the ATPase activity of TG2 with a concomitant reduction in its protein-crosslinking activity. We show that MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts secreted full-length TG2 and major smaller fragments of 66 and 56 kDa, the latter having ATP-binding abilities. MT1-MMP inhibition by a neutralizing antibody suppressed mineralization of osteoblast cultures to 35% of control, and significantly reduced phosphate levels in conditioned medium (CM). Furthermore, MT1-MMP inhibition abolished two of TG2 fragments in the cultures, one of which, the 56-kDa fragment, has ATPase activity. Neutralization of MT1-MMP at early phases of mineralization significantly reduced mineral deposition, but had no effect in later phases implying MT1-MMP and TG2 might contribute to the initiation of mineralization. The cleavage of TG2 by MT1-MMP likely occurs on the cell surface/pericellular matrix where MT1-MMP and TG2 were co-localized. Based on these data, we propose that MT1-MMP modulates the extracellular function TG2 as part of a regulatory mechanism activates the pro-mineralization function of TG2. | | 20049897
 |
High-throughput identification of IMCD proteins using LC-MS/MS.
Pisitkun, T; Bieniek, J; Tchapyjnikov, D; Wang, G; Wu, WW; Shen, RF; Knepper, MA
Physiological genomics
25
263-76
2006
Show Abstract
The inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) is an important site of vasopressin-regulated water and urea transport. Here we have used protein mass spectrometry to investigate the proteome of the IMCD cell and how it is altered in response to long-term vasopressin administration in rats. IMCDs were isolated from inner medullas of rats, and IMCD proteins were identified by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). We present a WWW-based "IMCD Proteome Database" containing all IMCD proteins identified in this study (n = 704) and prior MS-based identification studies (n = 301). We used the isotope-coded affinity tag (ICAT) technique to identify IMCD proteins that change in abundance in response to vasopressin. Vasopressin analog (dDAVP) or vehicle was infused subcutaneously in Brattleboro rats for 3 days, and IMCDs were isolated for proteomic analysis. dDAVP and control samples were labeled with different cleavable ICAT reagents (mass difference 9 amu) and mixed. This was followed by one-dimensional SDS-PAGE separation, in-gel trypsin digestion, biotin-avidin affinity purification, and LC-MS/MS identification and quantification. Responses to vasopressin for a total of 165 proteins were quantified. Quantification, based on semiquantitative immunoblotting of 16 proteins for which antibodies were available, showed a high degree of correlation with ICAT results. In addition to aquaporin-2 and gamma-epithelial Na channel (gamma-ENaC), five of the immunoblotted proteins were substantially altered in abundance in response to dDAVP, viz., syntaxin-7, Rap1, GAPDH, heat shock protein (HSP)70, and cathepsin D. A 28-protein vasopressin signaling network was constructed using literature-based network analysis software focusing on the newly identified proteins, providing several new hypotheses for future studies. | | 16449382
 |
Automated quantification tool for high-throughput proteomics using stable isotope labeling and LC-MSn.
Guanghui Wang, Wells W Wu, Trairak Pisitkun, Jason D Hoffert, Mark A Knepper, Rong-Fong Shen, Guanghui Wang, Wells W Wu, Trairak Pisitkun, Jason D Hoffert, Mark A Knepper, Rong-Fong Shen
Analytical chemistry
78
5752-61
2006
Show Abstract
LC-MSn has become a popular option for high-throughput quantitative proteomics, thanks to the availability of stable-isotope labeling reagents. However, the vast quantity of data generated from LC-MSn continues to make the postacquisition quantification analyses challenging, especially in experiments involving multiple samples per experimental condition. To facilitate data analysis, we developed a computer program, QUIL, for automated protein quantification. QUIL accounts for the dynamic nature of spectral background and subtracts this background accordingly during ion chromatogram reconstruction. For elution profile identification, QUIL minimizes the inclusion of coeluted neighbor peaks, yet tolerates imperfect peak shapes. Outlier-resistant methods have been implemented for better protein ratio estimation. The utility of QUIL was validated by quantitative analyses of a standard protein as well as complex protein mixtures, which were labeled with cICAT or 18O and analyzed using LCQ, LTQ, or FT-ICR instruments. For samples that no prior knowledge of relative protein quantities was available, Western blotting was performed for confirmation. For the standard protein, the coefficient of variation (CV) of peptide ratio estimation was 6%. For complex mixtures, the median CV for protein ratio calculations was less than 10%. Computed protein abundance ratios exhibited a relatively high degree of correlation with those obtained from Western blot analyses. Compared with a widely used commercial software tool, QUIL showed improvement in ion chromatogram construction and peak integration and significantly reduced relative errors in abundance ratio assessment. | | 16906720
 |
Transglutaminase 2-/- mice reveal a phagocytosis-associated crosstalk between macrophages and apoptotic cells.
Szondy, Zsuzsa, et al.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 100: 7812-7 (2003)
2003
Show Abstract
Tissue transglutaminase (TGase2) is a protein-crosslinking enzyme known to be associated with the in vivo apoptosis program. Here we report that apoptosis could be induced in TGase2-/- mice; however, the clearance of apoptotic cells was defective during the involution of thymus elicited by dexamethasone, anti-CD3 antibody, or gamma-irradiation, and in the liver after induced hyperplasia. The lack of TGase2 prevented the production of active transforming growth factor-beta1 in macrophages exposed to apoptotic cells, which is required for the up-regulation of TGase2 in the thymus in vivo, for accelerating deletion of CD4+CD8+ cells and for efficient phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies. The deficiency is associated with the development of splenomegaly, autoantibodies, and immune complex glomerulonephritis in TGase2-/- mice. These findings have broad implications not only for diseases linked to inflammation and autoimmunity but also for understanding the interrelationship between the apoptosis and phagocytosis process. | Immunoblotting (Western) | 12810961
 |
Targeted inactivation of Gh/tissue transglutaminase II.
Nanda, N; Iismaa, SE; Owens, WA; Husain, A; Mackay, F; Graham, RM
The Journal of biological chemistry
276
20673-8
2001
Show Abstract
The novel G-protein, G(h)/tissue transglutaminase (TGase II), has both guanosine triphosphatase and Ca(2+)-activated transglutaminase activity and has been implicated in a number of processes including signal transduction, apoptosis, bone ossification, wound healing, and cell adhesion and spreading. To determine the role of G(h) in vivo, the Cre/loxP site-specific recombinase system was used to develop a mouse line in which its expression was ubiquitously inactivated. Despite the absence of G(h) expression and a lack of intracellular TGase activity that was not compensated by other TGases, the Tgm2(-/-) mice were viable, phenotypically normal, and were born with the expected Mendelian frequency. Absence of G(h) coupling to alpha(1)-adrenergic receptor signaling in Tgm2(-/-) mice was demonstrated by the lack of agonist-stimulated [alpha-(32)P]GTP photolabeling of a 74-kDa protein in liver membranes. Annexin-V positivity observed with dexamethasone-induced apoptosis was not different in Tgm2(-/-) thymocytes compared with Tgm2(+/+) thymocytes. However, with this treatment there was a highly significant decrease in the viability (propidium iodide negativity) of Tgm2(-/-) thymocytes. Primary fibroblasts isolated from Tgm2(-/-) mice also showed decreased adherence with culture. These results indicate that G(h) may be importantly involved in stabilizing apoptotic cells before clearance, and in responses such as wound healing that require fibroblast adhesion mediated by extracellular matrix cross-linking. | | 11274171
 |
Villous cytotrophoblast regulation of the syncytial apoptotic cascade in the human placenta.
B Huppertz, H G Frank, J C Kingdom, F Reister, P Kaufmann, B Huppertz, H G Frank, J C Kingdom, F Reister, P Kaufmann
Histochemistry and cell biology
110
495-508
1998
Show Abstract
Villous trophoblast in the human placenta consists of a population of proliferating stem cells which differentiate and individually fuse into the syncytiotrophoblast. We studied the apoptotic cascade in this complex epithelial layer by immunohistochemical localization of Fas, FasL, Bcl-2, Mcl-1, pro-caspase-3 and caspase-3, T-cell-restricted intracellular antigen-related protein (TIAR), poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), lamin B, topoisomerase IIalpha, and transglutaminase II in cryostat and paraffin-fixed tissue sections from normal human first-trimester and term placental villi. The relationship between the apoptotic cascade and syncytial fusion was studied by coincubation of intact villi with FITC-coupled annexin-V, to detect the phosphatidylserine flip, and propidium iodide, to detect plasma membrane permeability. The final events of the apoptotic cascade were studied by the TUNEL reaction and ultrastructural appearance of the trophoblast. The phosphatidylserine flip was identified in some of the villous cytotrophoblastic cells, but the presence of both Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins presumably prevented continuation of the apoptotic cascade. The syncytiotrophoblast demonstrated heterogeneous findings, suggesting variable progression along the apoptotic cascade. In some areas Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 predominated, with preservation of the nuclear proteins PARP, lamin B, and topoisomerase IIalpha; in other areas, especially in and around syncytial sprouts, Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 were absent, accompanied by loss of nuclear proteins, presence of phosphatidylserine flip, and TUNEL positivity. These data suggest that the apoptotic cascade is initiated in the villous cytotrophoblast, which in turn promotes syncytial fusion. Donation of anti-apoptotic proteins into the syncytium, such as Bcl-2 and Mcl-1, focally inhibits further progression along this cascade. Completion of the apoptotic cascade takes place in and around syncytial sprouts, providing further evidence that these are the sites of trophoblast shedding into the maternal circulation. | | 9826129
 |
Retinoid-regulated expression of BCL-2 and tissue transglutaminase during the differentiation and apoptosis of human myeloid leukemia (HL-60) cells
Nagy, L., et al
Leuk Res, 20:499-505 (1996)
1996
| Immunocytochemistry | 8709622
 |